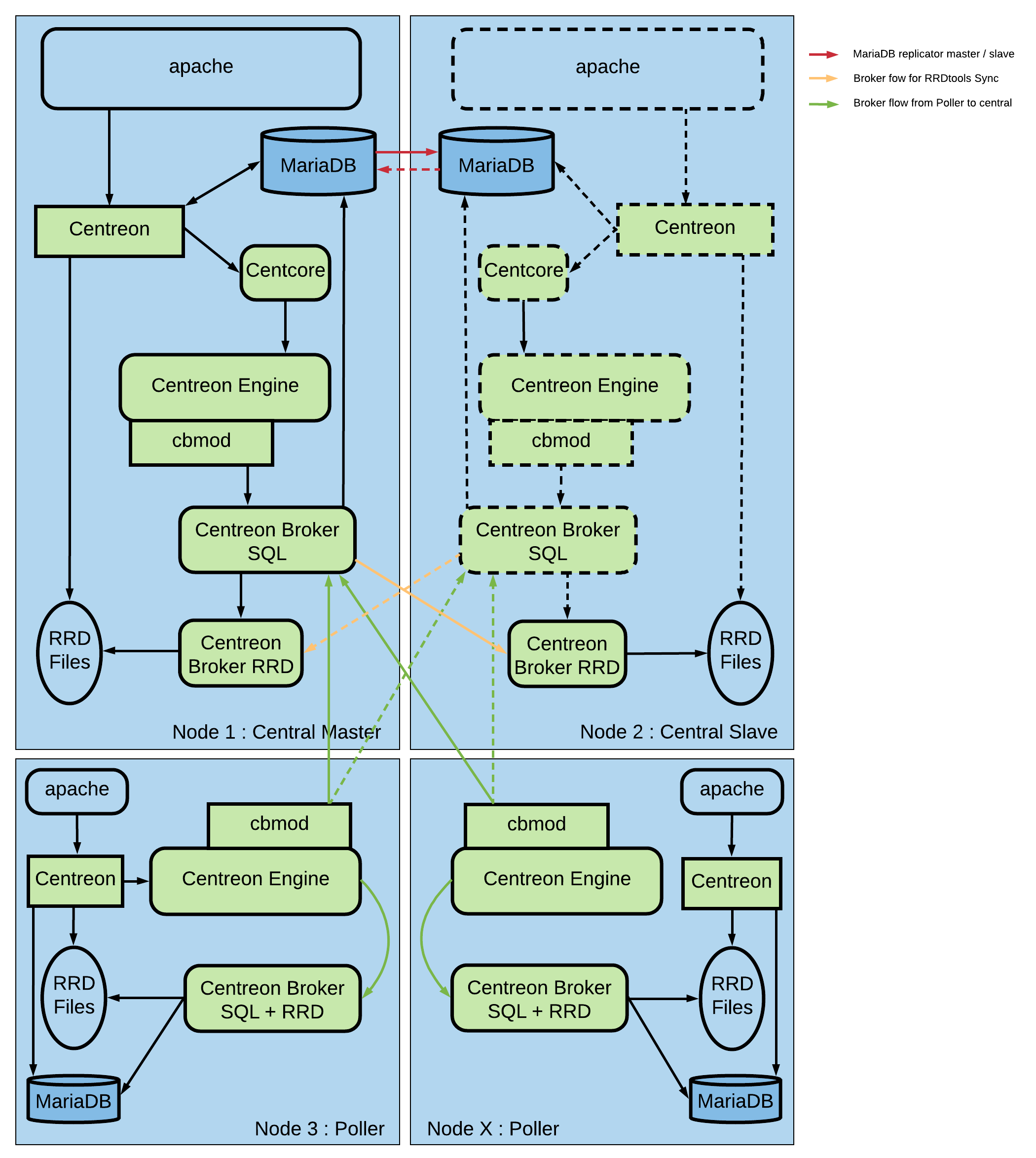
Distributed architecture with failover and web GUI for remote server¶
Description¶
The distributed architecture with remote DBMS is to have three types of entities:
A central Centreon server to display information
One or more remote servers to collect data
In order to have a failover the centreon central server is duplicated. This architecture allows to have a local web display only interface of Centreon on each remote server. Users can connect to read-only local web interface of remote servers to access to local monitoring data.
The central Centreon server includes the following items:
Centreon web interface
Monitoring Engine
Broker
Databases (MySQL + RRD)
The remote servers include the following items:
Centreon read-only local web interface
Monitoring Engine
Databases (MySQL + RRD)
Broker module to forward collected data to a central broker
This architecture is used for:
Enable load balancing across multiple remote monitoring servers
Network streams isolation: if your monitoring architecture has to monitor a DMZ area, it is easier (and safe) to place a remote server in the DMZ network
Have a failover system: if the master centreon server is DOWN the other one allows to continue to display data.
Have a read-only interface on each poller to have access to locally collected data if a failure connection appears between remote server and Centreon central server.
Components¶
Central Centreon server¶
There is two types of Centreon central server:
A master server
A slave server which is configured as the master one but with only MySQL and Centreon Broker RRD monitoring processes started.
Many components are used to build a master Centreon server:
Apache web server for Centreon web interface
The central Centreon server get configuration and collected data from DBMS server
The Centcore process is used to send monitoring configuration to the remote server and to manage it
A monitoring engine to collect data
Collected data are sent to Centreon Broker SQL using cbmod by monitoring engine
Centreon Broker SQL allows to store information into MariaDB databases and forward them to the two Centreon Broker RRD (master and slave)
Centreon Broker RRD generates and updates RRD files with data in order to display performance graphs
A MySQL replication allows to store in both databases Centreon configuration and collected data.
The slave server is used in regular mode to generate and to update RRD files with data in order to display performance graphs.
In case of failure, the operator has to start the following process on slave server: Apache, CentCore, Centreon Engine and Centreon Broker SQL. The slave server becomes master.
The failover and the management of components are made by Corosync / Pacemaker system.
Remote monitoring server¶
Many components are used to build a remote server:
A monitoring engine to collect data
Collected data are sent to Centreon Broker SQL VIP using cbmod by monitoring engine and locally.
Centreon Broker SQL allows to store information into MariaDB databases and forward them to Centreon Broker RRD
Centreon Broker RRD generates and updates RRD files with data in order to display performance graphs